In the bustling concrete jungles of today’s urban landscapes, the concept of vertical gardens has emerged as a revolutionary solution to the challenges of space constraints and environmental sustainability. As an avid supporter of innovative urban agriculture practices, I’ve witnessed firsthand how vertical gardens are reshaping the way we think about food production in cities.
Vertical gardens, with their ability to transform bare walls into vibrant green spaces teeming with life, not only enhance the aesthetic appeal of urban environments but also offer a practical approach to growing fresh produce locally. In this article, I’ll delve into the transformative impact of vertical gardens on urban agriculture and explore how this trend is revolutionizing the way we cultivate crops in limited spaces.
Understanding Vertical Gardens
Vertical gardens are innovative structures designed to maximize space utilization by growing plants vertically, making them an excellent solution for urban areas with limited space. These gardens offer a sustainable approach to urban agriculture, transforming empty walls into lush green spaces for cultivating various crops.
What Are Vertical Gardens?
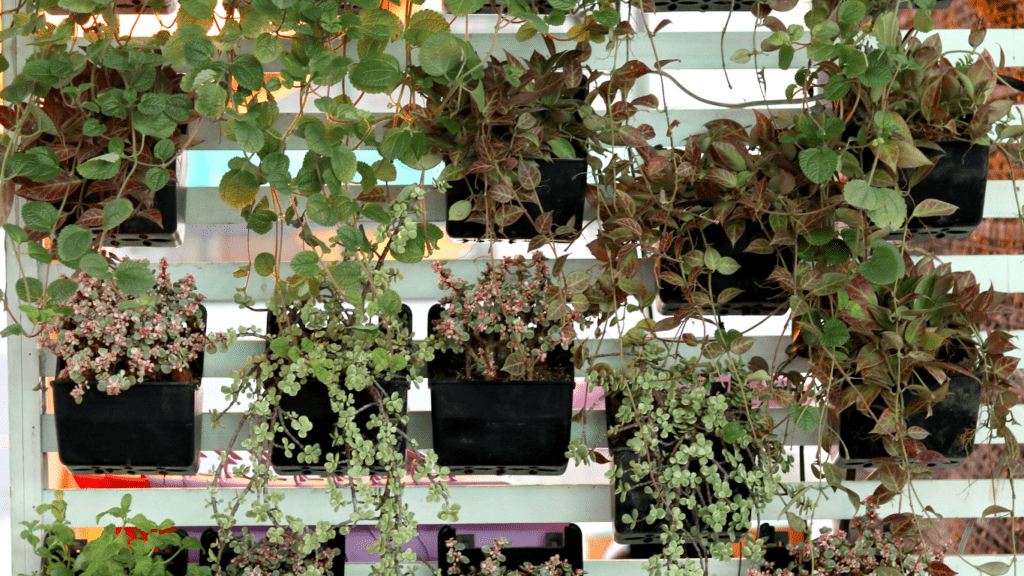
Vertical gardens, also known as living walls or green walls, are vertical structures that support plant growth either indoors or outdoors. They consist of modular panels with pockets or containers where plants can grow vertically. The plants receive water and nutrients through a built-in irrigation system, promoting healthy growth.
The History of Vertical Gardening
The concept of vertical gardening dates back centuries, with ancient civilizations like the Babylonians and Aztecs using vertical structures to cultivate plants. However, modern vertical gardening gained popularity in the 20th century as a response to urbanization and limited land availability. Innovations in materials and technology have further advanced vertical gardening techniques, making them a prominent feature in contemporary urban agriculture.
Benefits of Vertical Gardens in Urban Areas
Vertical gardens bring numerous advantages to urban areas, serving as a game-changer in urban agriculture. Let’s delve into the benefits they offer:
Space Efficiency
Vertical gardens optimize space utilization in urban environments. By growing plants vertically, these innovative structures maximize limited space, making them ideal for urban settings with minimal land availability. They allow for the cultivation of a variety of plants without requiring large horizontal areas, making them a sustainable solution for urban agriculture.
Reduction in Urban Heat
Vertical gardens play a crucial role in reducing urban heat levels. By covering vertical surfaces with greenery, they help mitigate the urban heat island effect, where cities experience higher temperatures due to the concentration of buildings and concrete surfaces. The plants in vertical gardens provide shade, absorb sunlight, and release moisture through transpiration, cooling the surrounding area and creating a more pleasant microclimate.
Improved Air Quality
One significant advantage of vertical gardens is their contribution to improved air quality in urban areas. Plants in vertical gardens act as natural air filters, absorbing pollutants and particulate matter from the air. By photosynthesizing, they release oxygen and enhance air quality, creating healthier environments for urban dwellers. Vertical gardens help combat air pollution and promote a greener, more sustainable urban ecosystem.
Key Components of Vertical Gardens
Vertical gardens are intricate structures that consist of several key components. Here, I’ll delve into the structural elements, irrigation systems, and plant selection crucial in the successful implementation of vertical gardens.
- Structural Elements
When creating a vertical garden, the structural elements are fundamental. These include the framework, support structure, growing medium, and plant containers. The framework provides stability, the support structure holds the weight of the garden, the growing medium nourishes the plants, and the plant containers hold the vegetation in place. - Irrigation Systems
Efficient irrigation systems are essential for vertical gardens due to their unique vertical orientation. Drip irrigation is commonly used to deliver water and nutrients directly to the plants’ roots, ensuring optimal growth. Additionally, automated irrigation systems with timers and moisture sensors help maintain the right moisture levels, promoting plant health.
Plant Selection
Choosing the right plants is crucial for the success of a vertical garden. Consider factors such as light availability, water needs, and space constraints when selecting plants. Opt for a mix of trailing, climbing, and compact plants to create a visually appealing and diverse vertical garden that thrives in its urban environment.
Challenges Faced by Vertical Gardening
Vertical gardening, although innovative and space-efficient, comes with its own set of challenges that need to be addressed for successful implementation.
Maintenance Issues
Maintaining vertical gardens requires attention to detail and consistent care. Issues such as proper watering schedules, pest control, and regular pruning are essential to ensure the health and vitality of the plants. Without adequate maintenance, vertical gardens can quickly deteriorate, impacting their visual appeal and overall effectiveness in urban agriculture.
Cost Concerns
One of the significant challenges of vertical gardening is the initial cost involved in setting up and maintaining the system. From purchasing materials for the structure to installing irrigation systems and selecting suitable plants, the expenses can add up. However, it’s important to consider the long-term benefits and savings in terms of reduced energy consumption and improved environmental impact that vertical gardens can offer.
Climatic Limitations
Climatic conditions pose a considerable challenge to vertical gardening, especially in regions with extreme temperatures or limited sunlight. Plants in vertical gardens are more exposed to environmental elements, making them susceptible to fluctuations in temperature and light. Choosing resilient plant species and implementing climate control measures are crucial to overcoming climatic limitations and ensuring the success of vertical gardens in urban agriculture.
Case Studies: Successful Urban Vertical Gardens
In this section, I’ll delve into specific case studies that highlight successful implementations of urban vertical gardens.
Example in New York City
In New York City, the iconic One Central Park boasts a breathtaking vertical garden designed by renowned botanist Patrick Blanc. This living masterpiece spans the south and west facades of the building, covering over 3,000 square meters with more than 35,000 plants. The vertical garden not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of the structure but also serves practical purposes by reducing the building’s energy consumption and mitigating the urban heat island effect.
Example in Singapore
Singapore, known for its innovative approach to sustainability, features the award-winning Parkroyal on Pickering hotel with striking vertical gardens. Designed to mimic the natural landscape of terraced rice paddies, these green walls not only provide a lush green backdrop but also contribute to the local biodiversity and ecological balance. The hotel’s vertical gardens have become a prominent symbol of green urban architecture, setting a benchmark for sustainable building design in dense urban environments.
























































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































 Joseph Hood is an integral part of the project team, specializing in renewable energy and sustainable technology. His expertise in solar energy systems and energy efficiency plays a crucial role in shaping the project's goals and initiatives. Joseph actively collaborates with fellow team members to explore innovative solutions for reducing carbon footprints and promoting cleaner energy sources. His enthusiasm for public education ensures that community members are informed about the benefits of renewable energy, reinforcing the project's mission to create a more sustainable future.
Joseph Hood is an integral part of the project team, specializing in renewable energy and sustainable technology. His expertise in solar energy systems and energy efficiency plays a crucial role in shaping the project's goals and initiatives. Joseph actively collaborates with fellow team members to explore innovative solutions for reducing carbon footprints and promoting cleaner energy sources. His enthusiasm for public education ensures that community members are informed about the benefits of renewable energy, reinforcing the project's mission to create a more sustainable future.